May 1, 2025
Infrasound and its effects on humans and animals
Infrasound is sound with very long wavelengths, a planar wave structure and outside the range of normal hearing for moderate sound pressure levels. The attenuation of infrasound is complex; it initially increases with distance from the source (becoming quieter), but it can decrease over still further distances so that it then gets louder. When it interacts with buildings, it can produce secondary structural vibrations that may be perceptible to the occupants. Infrasound from wind turbines is particularly annoying because the sound signature contains short, frequent episodes and it persists over extended periods, compared with other short-duration sources (such as trains). Most people can ‘tune out’ repeated sounds but in some people the central nervous system becomes sensitized and they suffer the symptoms of chronic noise stress such as anxiety, depression, cognitive dysfunction and disrupted sleep (source: Wind turbine infrasound: Phenomenology and effect on people, ScienceDirect).
Why legacy wind turbines cause infrasound
The main cause of infrasound waves are the high velocity blades spinning beside the large diameter tower. This produces strong air compression/decompression waves, resulting in infrasound.
 |
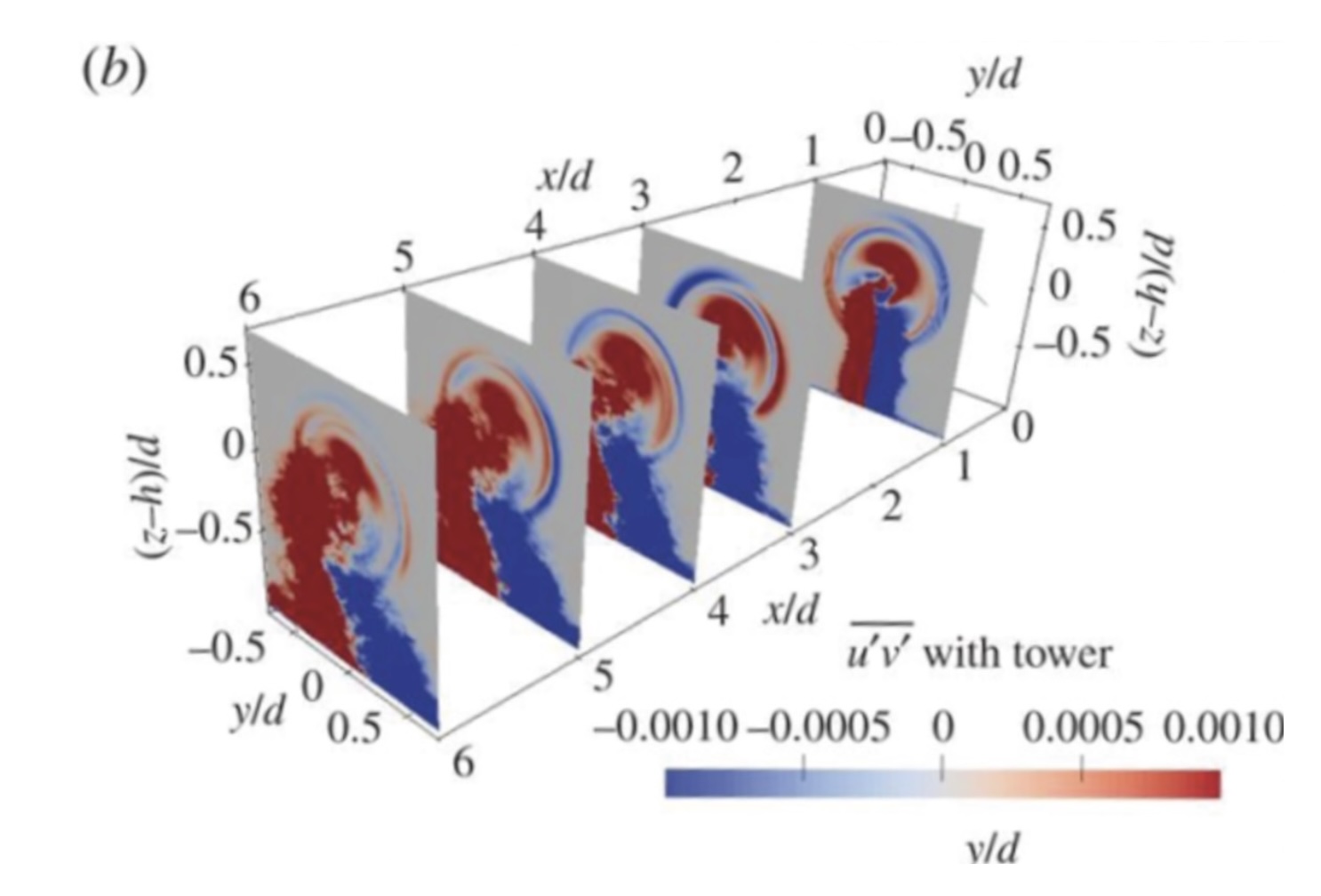 |
| Origin of infrasound waves | A model of sound waves produced by legacy wind turbines |
WindNext design eliminates infrasound
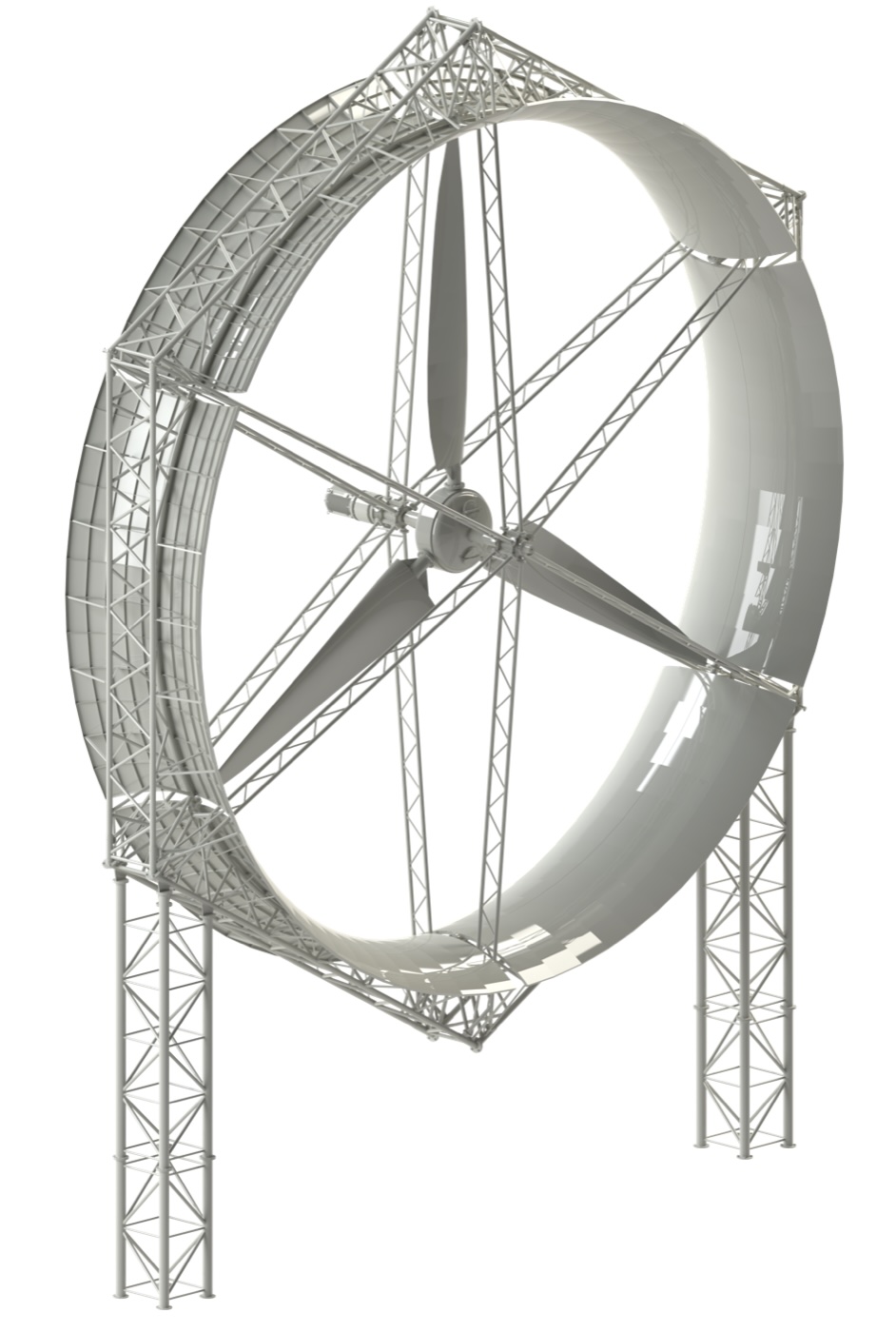
WindNext uses a frame design instead of a tower design, which eliminates the main cause of the infrasound. The rotor spins with speeds between 12 RPM and 60 RPM, which makes it impossible for the rotor to create sound frequencies lower than 20 Hz. These design fratures combine to eliminate harmful infrasound.
 |
 |
| WindNext design | A model of sound waves produced by WindNext turbine |

